티스토리 뷰
문제 링크
https://algospot.com/judge/problem/read/JAEHASAFE
algospot.com :: JAEHASAFE
Jaeha’s Safe 문제 정보 문제 문제 PDF 입력 . 출력 . 예제 입력 2 3 abbab babab ababb bbaba 2 RMDCMRCD MRCDRMDC DCMRCDRM 예제 출력 6 10 노트
algospot.com
현재 상태에서 타겟 상태로 가는 길이를 환형 시프트로 구현해야되는데
이를 kmp 알고리즘으로 간단히 구할 수 있습니다.
먼저 아래와 같은 예시에서 시계방향으로 가는 경우 타겟을 두 번 이어붙여서 kmp 알고리즘을 실행하면 이동 횟수를 구할 수 있습니다.

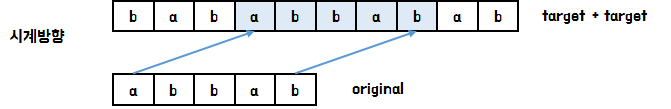
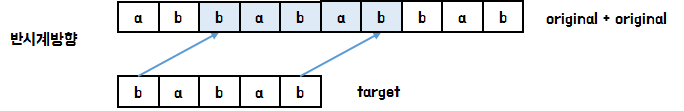
반시계방향인 경우 현재 상태를 두 번 이어붙여서 kmp 알고리즘을 실행시키면 마찬가지로 이동 횟수를 구할 수 있습니다.
구현 코드
'Coding Test > 알고스팟' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++] 알고스팟/접미사 배열 - 말버릇 (0) | 2020.09.04 |
|---|---|
| [C++] 알고스팟/문자열 검색 - 팰린드롬 만들기 (0) | 2020.09.02 |
| [C++] 알고스팟/문자열 검색 - 작명하기 (0) | 2020.09.01 |
| [C++] 알고스팟/탐욕법 - 문자열 합치기 (0) | 2020.08.31 |
| [C++] 알고스팟/탐욕법 - Microwaving Lunch Boxes (0) | 2020.08.28 |
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
링크
TAG
- Sqoop
- python
- 스파크
- 코딩인터뷰 완전분석
- Django
- import
- 백준
- pyspark
- 배열과 문자열
- 알고스팟
- 팰린드롬 구하기
- 외발 뛰기
- Hadoop
- C++
- 합친 lis
- 하이브
- HDFS
- 삼각형 위의 최대 경로
- Jaeha's Safe
- hive
- 2225
- 삼각형 위의 최대 경로 수 세기
- 출전 순서 정하기
- 완전탐색
- microwaving lunch boxes
- 분할정복
- HiveQL
- 하둡
- 두니발 박사의 탈옥
- 종만북
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
글 보관함
